Have you ever pondered the evolutionary journey of the simple yet critical component – the lock button? From the rudimentary keys of ancient Egypt to the sophisticated fingerprint scanners of today, the lock button has traversed an extraordinary timeline of innovation.

Image: www.knivesandtools.be
A Historical Perspective
The concept of securing valuable possessions dates back to the dawn of civilization. In ancient Egypt, exquisitely crafted keys adorned with hieroglyphics controlled access to sacred tombs and royal chambers. These keys, often made of wood or metal, employed intricate mechanisms to engage with wooden bolts or pins. Over time, key design evolved, with the Romans implementing warded locks featuring angled grooves that prevented unauthorized keys from turning.
The Lever Lock Revolution
A breakthrough occurred in the 17th century with the invention of the lever lock by Robert Barron. This innovative design utilized a series of levers that interacted with a bolt. The levers were lifted sequentially using a specific key pattern, significantly enhancing security. The lever lock’s durability and resistance to picking propelled it into widespread use. It remained a mainstay for centuries, securing homes, businesses, and government buildings.
The 20th Century: Technological Strides
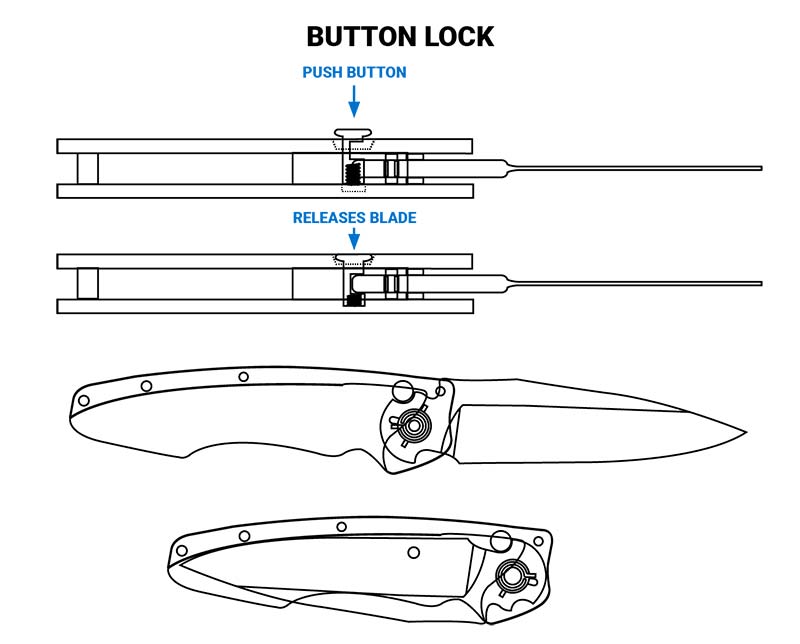
The 20th century witnessed a rapid acceleration in lock technology. In the 1920s, Linus Yale Jr. revolutionized lock-making with the pin tumbler lock. This design employed spring-loaded pins that aligned precisely when the correct key was inserted. The complexity of pin tumbler locks made them highly resistant to unauthorized entry.

Image: knivesngear.com
Modern Innovations: A Convergence of Advanced Technologies
Entering the 21st century, the lock button has evolved dramatically under the influence of electronics and digital technology. Electronic locks utilize keypads, proximity sensors, and even smartphone applications to control access. Smart locks, equipped with advanced encryption protocols and remote management capabilities, offer unprecedented levels of security and convenience.
Biometrics and Beyond: The Cutting Edge
Recent years have ushered in the era of biometric locks. Fingerprint and facial recognition systems eliminate the need for physical keys, providing unrivaled security by verifying a person’s unique biological traits. As technology continues to advance, we can anticipate even more sophisticated and user-friendly lock button solutions on the horizon.
Tips and Expert Advice for Lock Button Security
– Use Strong Passcodes or Key Combinations: Weak passwords are an invitation to hackers. Opt for complex combinations of letters, numbers, and symbols.
– Enable Two-Factor Authentication: This extra layer of security requires additional verification, such as a code sent to your phone, before granting access.
– Keep Software Updated: Stay ahead of potential vulnerabilities by regularly updating your electronic locks’ firmware and mobile applications.
Frequently Asked Questions on Lock Button Axis
Q: What is a lock button axis?
A: A lock button axis is a real or virtual line around which a lock button moves or operates. This axis determines the button’s orientation and the direction of movement.
Q: What are the benefits of using a lock button with an axis?
A: An axis provides stability and allows for precise control over the lock button’s movement, ensuring consistent and reliable operation.
Q: What is the difference between a two-axis and three-axis lock button?
A: A two-axis lock button can move along two perpendicular axes, typically horizontal and vertical, while a three-axis lock button adds movement along a third axis, allowing for diagonal or rotational movements.
Lock Button Axis
Conclusion
The lock button has come a long way since its humble origins, evolving to meet the changing needs of security and convenience. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more innovative and sophisticated lock button designs that enhance our homes, workplaces, and digital lives. Are you curious about how the lock button will continue to evolve in the future?
 Teknobae.com Berita Teknologi, Review Gadget, Laptop, Komputer, Smartphone, Handphone
Teknobae.com Berita Teknologi, Review Gadget, Laptop, Komputer, Smartphone, Handphone



